Blog de Zscaler
Reciba en su bandeja de entrada las últimas actualizaciones del blog de Zscaler
Suscríbase
Multiple Hijacking
Vulnerable websites are regularly hijacked to redirect users to malicious domains. The most popular type of of malicious page are Fake AV pages. Attackers commonly increase traffic to these hijacked websites using Blackhat SEO techniques.
Blackhat SEO requires that two different pages be delivered to different audiences:
- A harmless spam page to the Googlebot and security scanners, in order to get references and be ranked well by Google, as well as evade denylists
- A redirection to a malicious domain to attack users
Existing pages on the hijacked sites are usually unchanged and instead, new pages are created. The newly created spam pages are completely harmless, with no obfuscated JavaScript. A 302/307 HTTP redirection is done mostly via a PHP file, or using an .htaccess file.
Other groups of attackers may want to use vulnerable websites for different purposes. So it is not rare to see the same vulnerable sites being abused by different groups. Recently, there was an increase in hijacked websites sending users to Fake AV pages also being infected with malicious JavaScript. The obfuscated JavaScript code is added before the original HTML code on all pages, making it much more likely to be blocked by Google. Here are a few examples:
 |
| Found on dailygizmonews.com |
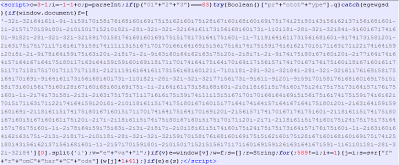 |
| Found on malaysianaspiration.com |
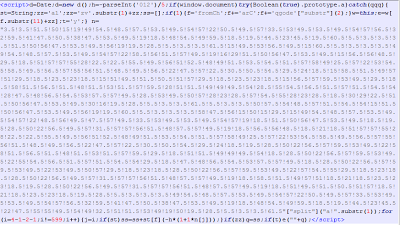 |
| A mix of the 2 previous JavaScript codes |
All of these examples result in the same HTML code, an IFRAME injection pointing to a malicious domain:
- hxxp://fbyvdtydyth.myfw.us/?go=2
- hxxp://tds46.lookin.at/stds/go.php?sid=1
- hxxp://qerhkbdimoitvd5t.lowestprices.at/?go=2
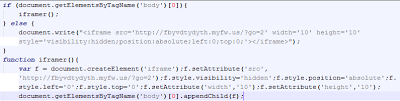 |
| Deofuscated code |
Ironically, this malicious code might actually keep user safer. Since it is present on all pages, regardless of the HTTP Referrer, the entire website is flagged as malicious much more quickly by search engines.
¿Este post ha sido útil?
Exención de responsabilidad: Este blog post ha sido creado por Zscaler con fines informativos exclusivamente y se ofrece "como es" sin ninguna garantía de precisión, integridad o fiabilidad. Zscaler no asume responsabilidad alguna por cualesquiera errores u omisiones ni por ninguna acción emprendida en base a la información suministrada. Cualesquiera sitios web de terceros o recursos vinculados a este blog se suministran exclusivamente por conveniencia y Zscaler no se hace responsable de su contenido o sus prácticas. Todo el contenido es susceptible a cambio sin previo aviso. Al acceder a este blog, usted acepta estas condiciones y reconoce su responsabilidad exclusiva de verificar y utilizar la información según sea precisa para sus necesidades.
Reciba en su bandeja de entrada las últimas actualizaciones del blog de Zscaler
Al enviar el formulario, acepta nuestra política de privacidad.




